how are work and energy related explain the work-energy theorem
10 N 10 kgms 2 so 10 J 10 kgm 2 s 2. The Work-Energy theorem is an important principle in science and many of the inventions and activities in the world are based on this crucial law.

The Work Energy Theorem Objectives Investigate Quantities Using The Work Energy Theorem In Various Situations Calculate Quantities Using The Work Energy Ppt Download
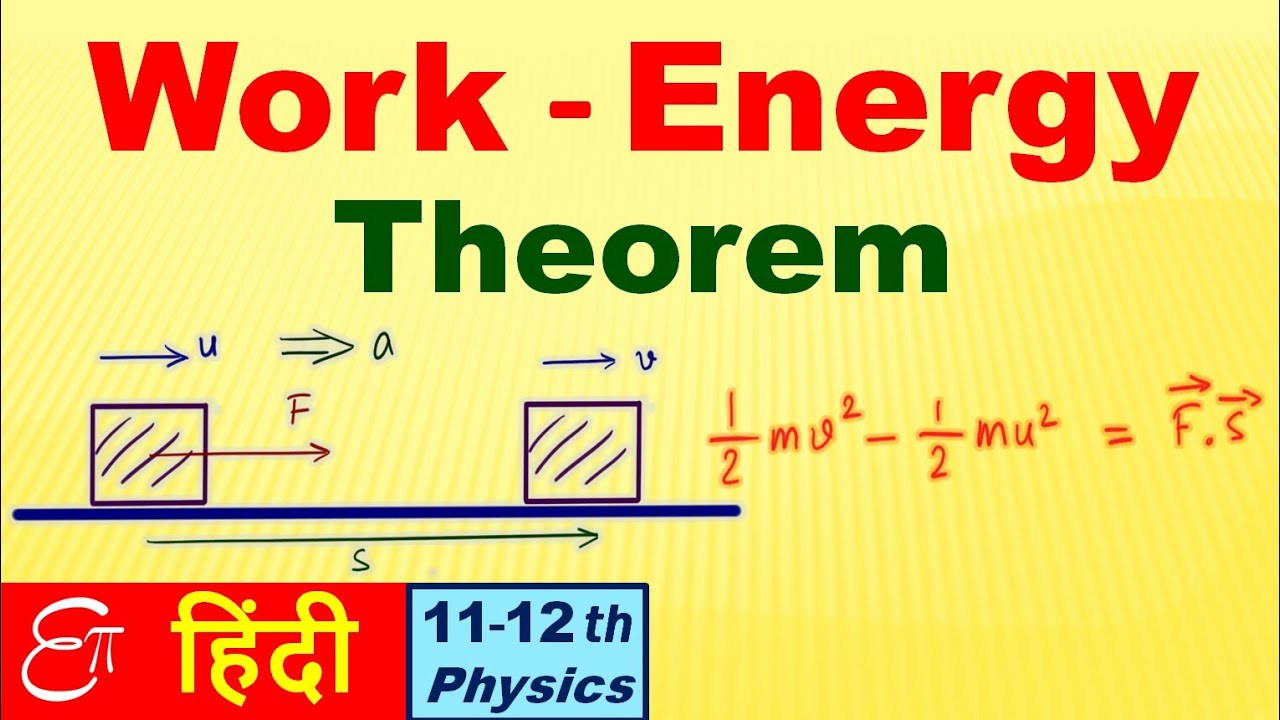
Wnet mvf2 - mvo2.

. K f K i W. Work relates to displacement and displacement relates to kinetic energy. When an objects velocity decreases the object has worked on the world and the objects energy decreases.
The result based on Newtons laws that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy kinetic energy. We will find that some types of work leave the energy of a system constant for example whereas others change the system in some way such as making it move. The work-energy theorem states that the change in the kinetic energy is equal to the amount of work done.
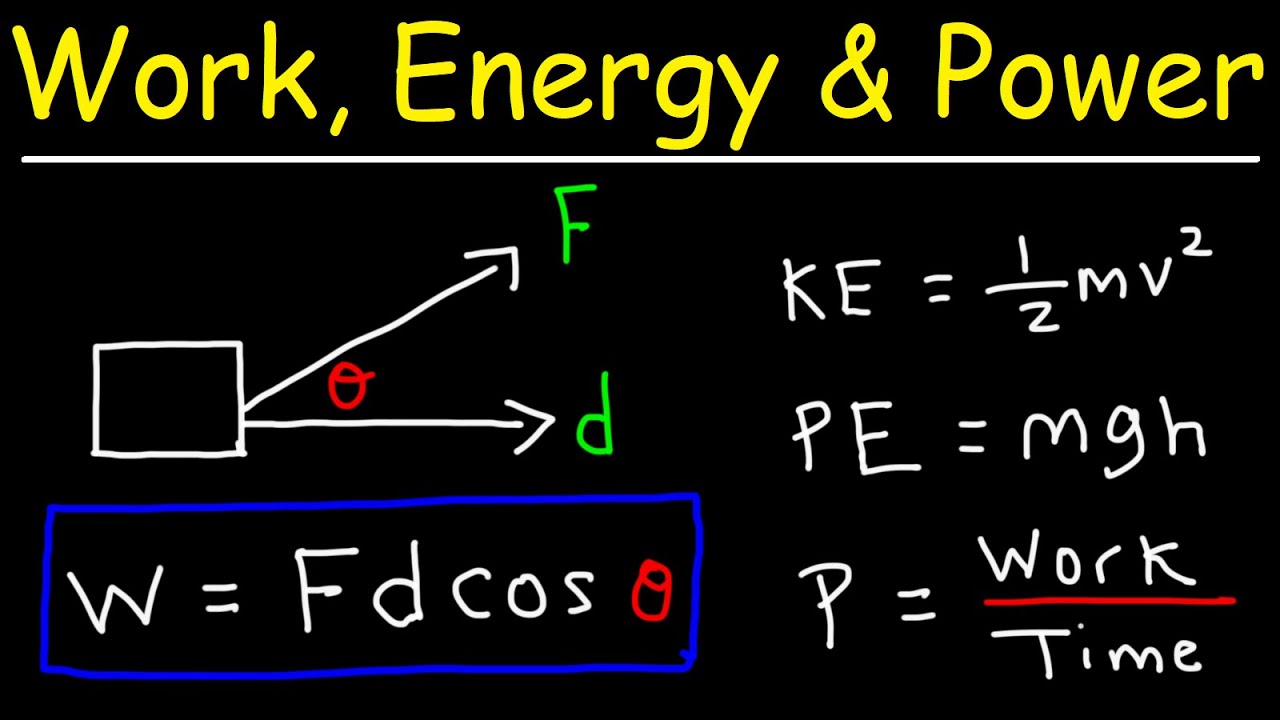
Work is said to be done whenever the force is applied to an object then the object is moved to a certain distance. 10 J 10 Nm the units of force multiplied by distance. To perform work energy has to be spent.
Wnet ma xf - xo Given uniform acceleration vf2 - vI2 2axf - xo. You might get tired if you keep standing for a long time. Work W - when a force causes displacement of an object.
The theorem implies that the net work on a system equals the change in the quantity latexfrac12mv2latex This quantity is our first. Equal to one half times mass times the square of the velocity of an object. F is the final kinetic energy and K.
The work-energy theorem also known as the principle of work and kinetic energy states that the total work done by the sum of all the forces acting on a particle is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of that particle. The work-energy theorem states that the net work done by the external forces on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object. Energy - the ability to do work.
53 Work-energy theorem ESCMD Conservative and non-conservative forces ESCMF. M is the mass of the object measured using kilograms. The work-energy theorem explains the idea that the net work - the total work done by all the forces combined - done on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object.
This explanation can be extended to rigid bodies by describing the work of rotational kinetic energy and torque. W net K. We will also develop definitions of important forms of energy such as the energy of.
The measurement of work and energy with the same unit reinforces the idea that work and energy are related and can be converted into one another. This equation is one form of the work-energy equation and gives us a direct relation between the net work done on a particle and that particles velocity. So according to the theorem statement we can define the work-energy theorem as follows.
The Work-Energy theorem simply says that within the absence of different forces the work carried out by a force is equal to its change in kinetic force. This definition can be extended to rigid bodies by defining the work of the torque and rotational kinetic energy. The working-energy theorem defines work as the energy change brought on by the velocity change.
The principle of work and kinetic energy also known as the work-energy theorem states that the work done by the sum of all forces acting on a particle equals the change in the kinetic energy of the particle. If K represents the change in kinetic energy of the body and W represents the work done on it. Kinetic energy KE - the energy of motion.
Substituting for axf - xo into our work equation we find that. Unless the displacement is in the reverse direction and the force applied. The energy an object has by reason of its motion equal to latexfrac12textmv2latex for the translational ie non-rotational motion of an object of mass m moving at speed v.
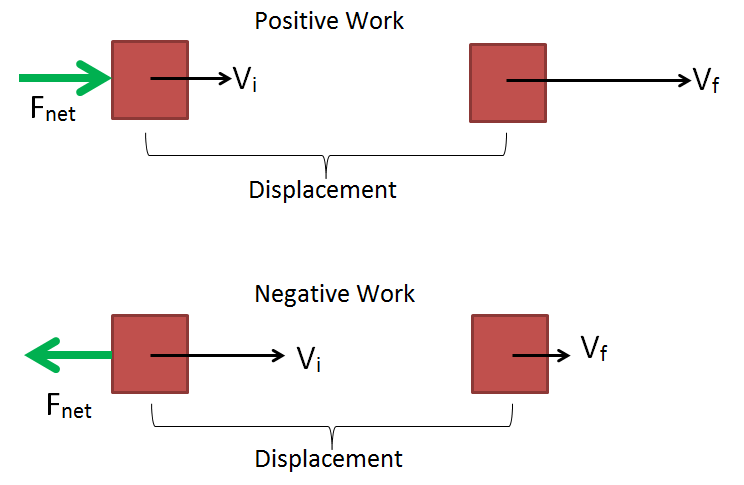
When the displacement and the force applied are in an opposite direction. If there is no displacement there is no work done. Potential energy also referred to as stored energy is the ability of a system to do work due to its position or internal structure.
The work-energy theorem affirms that the work done on any object is comparable to the difference in kinetic energy of the object. The Work-energy theorem explains the reasons behind this Physics of no work. This relationship is called the workenergy theorem.
The joule J is the metric unit of measurement for both work and energy. Energy is ability to do work. Work-energy theorem - this theorem states that the work done on an object will either add kinetic energy to an object or take kinetic.
O is the original kinetic energy. This expression is called the work-energy theorem and it actually applies in general even for forces that vary in direction and magnitude although we have derived it for the special case of a constant force parallel to the displacement. The work-energy theorem relates the net work done of forces on an object and the change in the kinetic energy of the object.
Examples are energy stored in a pile driver at the top of its path or energy. Learn about the definition and application of the work-energy theorem. After the net force is removed no more work is being done the objects total energy is altered as a result of the work that was done.
Translational kinetic energy is distinct from rotational kinetic energy which is considered later In equation form the. W 1 2 m v f 2 1 2 m v i 2. Work is said to be done when an acting force displaces a particle.
The net work on a system equals the change in the quantity. The quantity in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass moving at a speed Translational kinetic energy is distinct from rotational kinetic energy which is considered later. Work done by an object can be mathematically expressed as.
The environment has acted on the object and it increases the energy of the object. In Grade 10 you saw that mechanical energy was conserved in the absence of non-conservative forces. Where W is the work done by object measured using Joules.
Work and energy are directly proportional to each other. It is important to know whether a force is an conservative force or an non-conservative force in the system because this is related to whether the force can change an objects total mechanical. Where K f Final kinetic energy.
The quantity 1 2mv2 in the work-energy theorem is defined to be the translational kinetic energy KE of a mass m moving at a speed v.

Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Work And The Work Energy Principle Video Khan Academy
Work Energy Theorem Energy Education

A State And Prove Work Energy Theorem In The Case Of Const Scholr
Work Energy And Power Basic Introduction Youtube

Energy Work Power 16 Of 31 Work Energy Principle An Explanation Youtube

Homework And Exercises Can The Work Energy Theorem Be Applied In This Case Physics Stack Exchange

Work Energy Theorem Variable Force Youtube
Work Energy Theorem Work Energy Power 2 In Hindi Youtube

Homework And Exercises Can The Work Energy Theorem Be Applied In This Case Physics Stack Exchange
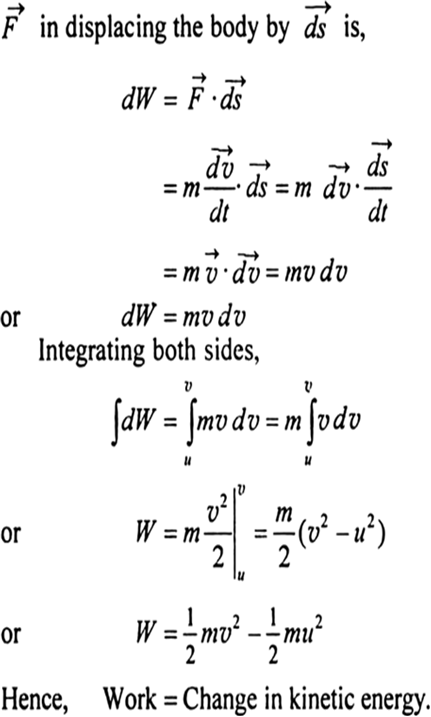
State And Prove Work Energy Relationship From Physics Work Energy And Power Class 11 Cbse

Work Energy Theorem Proof Constant Variable Force Video Examples

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem Physics

Kinetic Energy And The Work Energy Theorem Physics

Work Energy Theorem Review Article Khan Academy

Work Energy And Power Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 6 Learn Cbse
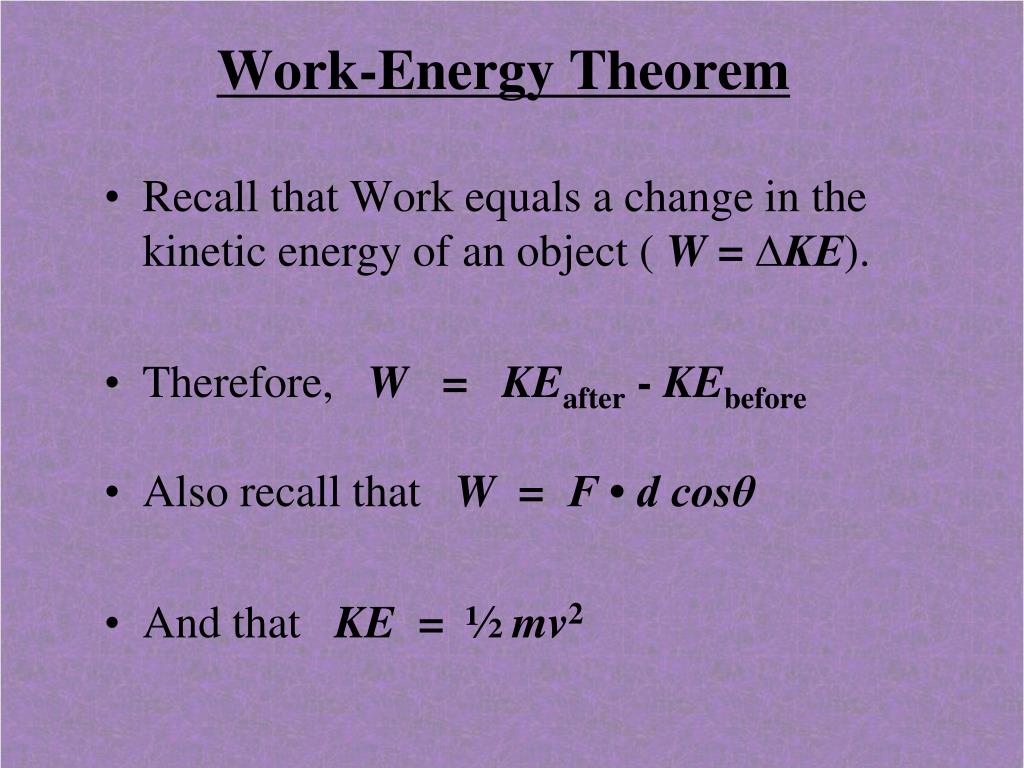
Ppt Work Energy Theorem Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5571805

Please Explain Me Work Energy Theorem With Its Proof Physics Topperlearning Com Bxhj4pii
